Estimation of Hemoglobin by Sahli method
Clinical Significance
A decrease in hemoglobin below normal range is an indication of anemia. An Increase in hemoglobin concentration occurs in hemoconcentration due to loss of body fluid in saver diarrhea and vomiting. High values are also observed in congenital heart disease (due to reduce oxygen supply) in emphysema and also in polycythemia. Hemoglobin concentration drops during pregnancy due to Hemodilution.
Normal Values
| Category | Normal Value |
| Men | 13 – 18 Hb, g/dl |
| Women | 12 – 16.5 Hb, g/dl |
| Children (up to 1 year) | 11.0 – 13.0 Hb, g/dl |
| Children (10 – 12 year) | 11.5 – 14.5 Hb, g/dl |
| Infants (full term cord blood) | 13.5 – 19.5 Hb, g/dl |
Method Name
Sahli (acid hematin) method
Principle
When blood is added to 0.1. N hydrochloric acid, hemoglobin is converted to brown coloured acid hematin. The resulting color after dilution is compared with standard brown glass reference blocks of a sahli hemoglobinometer.
Specimen
Capillary blood or throughly mixed, anticoagulated (EDTA or double oxalateed) venous blood. The specimen need not be a fasting sample. when blood is stored in the refrigerator (2 degrees Celsius to 8 degree Celsius). hemoglobin remains unchanged provide that the blood does not become infected (as shown by turbidity or discoloration).
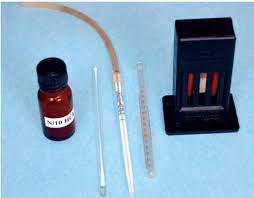
Requirements
- Sahli hemoglobinometer it consists of
- A standard brown glass mounted on a comparator
- A graduated tube (Hellige tube)
- Hb pipette (0.02ml)
- 0.1N hydrochloric acid
- Distilled water
- Pasteur pipettes
Procedure
- By using a Pasteur pipette add 0.1N hydrochloric acid in the tube up to the lowest mark, (20% mark).
- Draw blood up to 20 micro litre mark in the Hb pipette. Adjust the blood column, carefully without bubbles.
- Wipe excess of the blood on the sides of the pipette by using a dry piece of cotton (or gauge).
- Transfer blood to the acid in the graduated tube, rinse the pipette well, mix the reaction mixture and allow the tube to stand for at least 10 minutes.
- Dilute the solution with distilled water by adding few drops at a time carefully and by mixing the reaction mixture, until the colour matches with the glass plate in the comparator.
- The matching should be done only against natural light. The level of the fluid is noted at its lower meniscus and the reading corresponding to this level on the scale is recorded (blood hemoglobin, g/dl)
Additional Information
- Mathemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin and sulfhemoglobin are not converted to acid hematin by 0.1N hydrochloric acid.
- This method is useful for places where a photometer is not available.
- It can give an error up to 1 g/dl.
Precaution
Immediately after use rinse the Hb pipette by using tab water in a beaker. This prevents blocking of the pipette.
