Total Leukocyte Count (TLC) Test
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
Increase in total leukocyte count of more than 10,000/ Cumm ( micrometer ) is known as leukocytosis and decrease of less than 4,000 Cumm ( microlitter ) as leukopenia
Causes of Leukocytosis
- Pathological
It is common for a transient period in infections . The degree of rise in leukocytes depends on the type and severity of the infection and the response of the body . The infection may be
1 . Bacterial
2 . Viral
3 . Protozoal ( malaria )
4 . Parasitic ( filaria , hookworm infection ) .
Leukocytosis is also observed in severe hemorrhage and in leukemia .
- Physiological
1 . Age : At birth the total Leukocyte count is about 18,000 / Cumm ( microlitter) . It drops gradually to adult level .
2 . Pregnancy : At full term the total count tends to be about 12,000 to 15,000 / Cumm ( microlitter ) . It rises soon after delivery and then gradually returns to normal .
3 . High temperature .
4 . Severe pain .
5 . Muscular exercise .
Causes of leukopenia
certain viral and bacterial infections ( typhoid ) lead to leukopenia rather than leukocytosis .
1 . Infections
- Bacterial ( typhoid , paratyphoid , tuberculosis etc ) .
- Viral ( hepatitis , influenza , measles etc ) .
- Protozoal ( malaria )
2 . Some cases of leukemia .
3 . Primary bone marrow depression ( Aplastic anemia ) .
4 . Secondary bone marrow depression ( due to drugs , radiation etc ) .
5 . Anemia ( iron deficiency , megaloblastic etc ) .
NORMAL VALUES
| Adults | 4,000 – 10,000/ Cumm |
| At birth | 10, 000 – 25,000/ Cumm |
| 1 to 3 year’s | 6,000 – 18,000/Cumm |
| 4 to 7 year’s | 6,000 – 15,000/Cumm |
| 8 to 12 year’s | 4,500 – 13,500/Cumm |
SPECIMEN
1 . Double oxalate or EDTA blood
2 . Capillary blood ( The specimen need not be a fasting sample ) .
Total Red Blood Cells (RBC) Count
REQUIREMENTS
1 . Microscope
2 . Improved Neubauer chamber
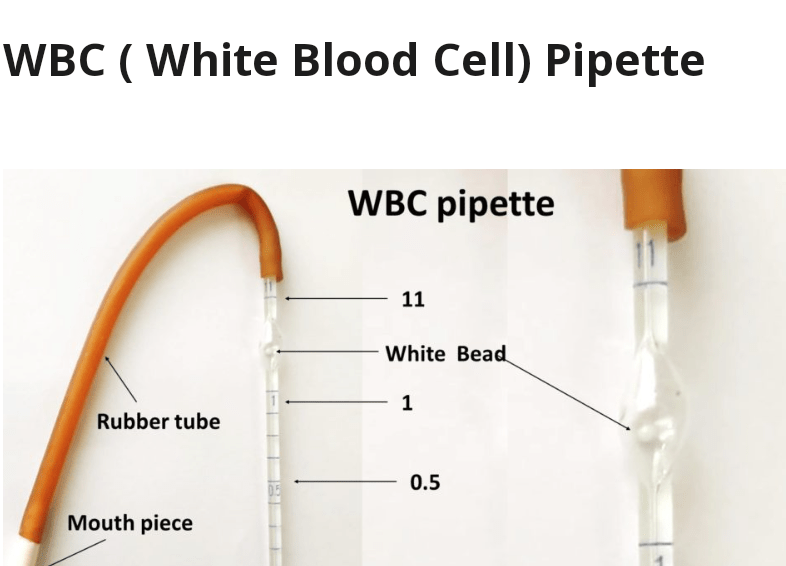
3 . WBC pipette
4 . WBC diluting fluid : it is prepared as follows
- Glacial Acetic acid = 2.0 ml
- 1% (w/v ) gentian violet = 1.0 ml
- Distilled water = 97 ml
This solution is stable at room temperature (25 ° C +_ 5°C ) . A pinch of thymol may be added as preservate .
PRINCIPLE
The glacial acid lyses the red cells while the gentian violet slightly stain the nuclei of the Leukocytes . The blood specimen is diluted 1: 20 in a WBC pipette with the diluting fluid and the cells are counted under low power of the microscope by using a counting chamber . The number of cells in undiluted blood are reported per Cumm ( microlitter ) of whole blood .
PROCEDURE
- Draw blood up to 0.5 mark of a WBC pipette .
- Carefully wipe excess blood outside the pipette by using cotton . Draw diluting fluid up to 11 Mark .
- Mix the contents in the pipette and after five minutes by discarding few drops fill the counting chamber and allow the cells to settle for two to three minutes .
Since bulb pipette are not recommended following procedure is performed
Make a 1:20 dilution of blood by adding 20 microlitter of blood to 0.38 ml of diluting fluid in a glass tube ( 10 × 75 mm ) . Cork the tube tightly and mix the suspension by rotating in a cell suspension mixed for at least 1 minute . Fill the Neubauer chamber by means of a pasteur pipette or glass capillary .
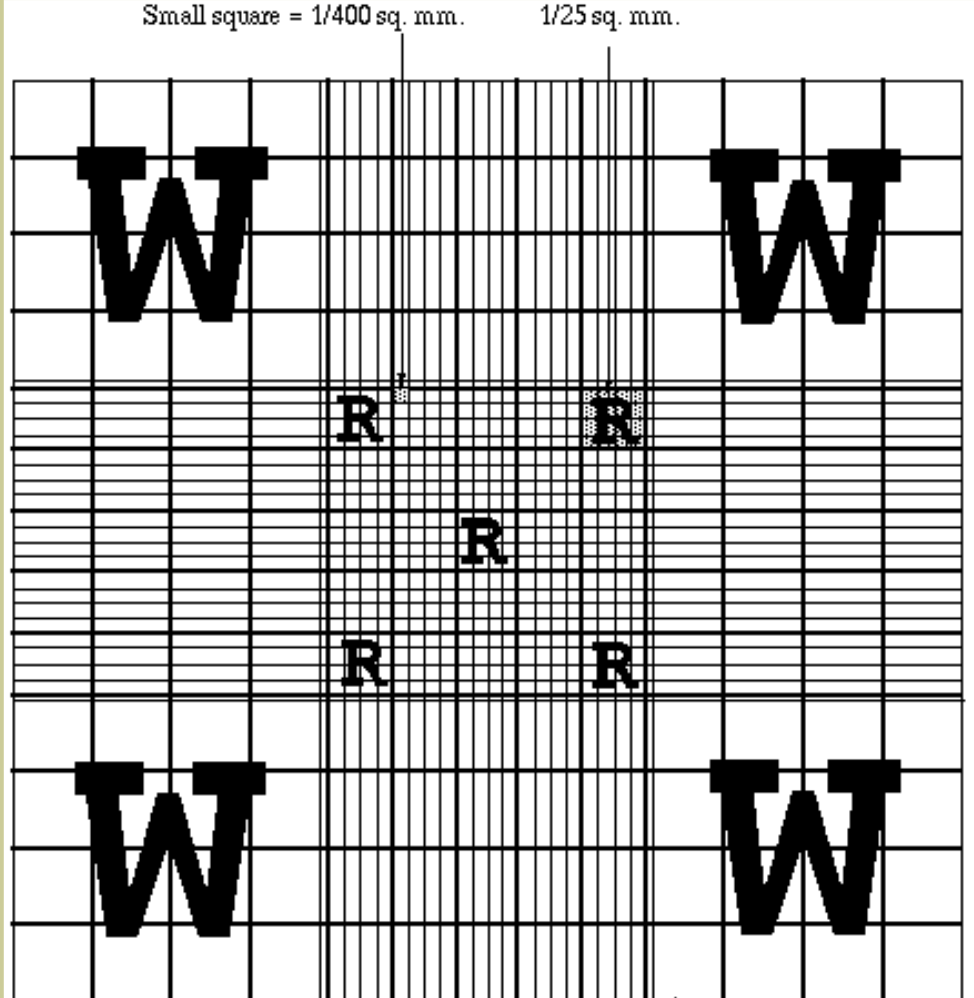
- Focus one of the `
W` marked areas ( each having 16 small squares ) by turning objective to low power ( 10 x ) . - Count cell in all four W marked corner .
- Calculation :
WBC count = number of white cells counted × dilution / area counted × depth of fluid
Error of the Total White cells Count
1 . The error as high as 20 % may make difference between 5.0 and 6.0 × 10⁹ cells per liter which is of little partical significance .
2 . The error can be reduced by counting more cells . If 400 cells are Counted the error is reduced to 5 % .
3 . Error may also be caused due to dirt clumped RBC debris or due to clumping of Leukocytes .
