Bleeding Time (BT) and Clotting Time (CT) Test
BLEEDING TIME (BT) TEST
Clinical Significance
Determination of bleeding time helps to detect vascular defect and platelet disorders. Prolonged. Breeding. Time. Is generally associated with thrombocytopenia. In case of von Willebrand disease, bleeding time is high with a normal platelet count. It is caused by a platelet defect combined with factor dfficiency. Clinical application of Bleeding time are following:-
- Thrombocytopenia
- Disorder of platelet functions
- Acute leukemias
- Aplastic anemias
- Liver disease
- Von Willebrand’s disease
- DIC
- Abnormality in the wall of blood vessels
- Administration of drugs prior to test e.g. aspirin.
Method
- Duke’s method.
- Finger Tip method.
- Ivy’s method.
Specimen
Blood collected by earlobe or finger puncture.
Principle
A 1 mm deep incision is made on the ear lope or finger of the patient. The length of time required for bleeding to cease is recorded.
Normal Range
1-5 minutes
Requirements
- Sterile lancet
- Spirit or 70% alcohol
- Circular filter paper
- Stopwatch
Procedure
- Clean the ear lobe (or finger) with spirit or alcohol by using a piece of cotton. Allow to dry.
- Puncher the earlobe or finger deeply about 1 mm by using sterile lancet. Start the stopwatch and the blood should flow freely without squeezing the ear lobe (or finger).
- After 30 seconds, collect the drop of blood at one corner of the filter paper. Do not touch the skin with the paper.
- Repeat step number 3 after every 30 seconds.
- When bleeding ceases, stop the stopwatch.
- Note the time on the.
Advantage
- The ear lobe abundant subcutaneous tissue and the is vascular.
- Flow of blood is quite good.
2. Finger Tip method procedure
- Clean the tip of a finger with sprite.
- Prick with a disposable needle or lancet.
- Start the stop-watch immediately.
- Start gently touching the pricked finger with a filter paper till blood spots continue to be made on the filter paper.
- Stop the watch when no more blood spot comes on the filter paper and note the time.
Disadvantages
- It is a crude method.
- Bleeding time is low by this method.
Normal bleeding time = 1-3 minutes
3. Ivy’s method procedure
- Tie the BP apparatus cuff around the patient upper arm and in flat it upto 40 mmHg which is maintained throughout the test.
- Clean an area with sprite over the flexor surface of forearm and let it dry.
- Using a disposable lancet or surgical blade make 2 puncture 3 mm deep 5-10 cm from each other taking care not to puncture the superficial veins.
- Start the stopwatch immediately.
- Go on blotting each puncture with a filter paper as in Duke’s method.
- Stop the watch, note the time in each puncture and calculate average bleeding time.
Advantage
- This is the method of choice.
- It is standardised method.
- Bleeding time is more accurate.
Normal bleeding time = 3-8 minutes
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Analysis
CLOTTING TIME (CT) TEST
Clinical Significance
This is also known as whole blood clotting time and is a major of plasma clotting factor. It is a screening test for coagulation disorder. Various other tests for coagulation disorders include prothrombin time (PT) Partial Thromboplatin time(PTTK) or Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTTK), and measurement of fibrinogen.
- Severe deficiency of coagulation factors
- Afibrinogenaemia
- Administration of heparin
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- Administration of drugs such as anticoagulant
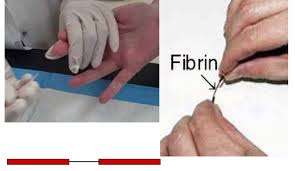
Method
- Capillary tube method.
- Lee-White method.
Normal Range
4 – 9 minutes
Specimen
Capillary blood
Principle
Blood is collected in a capillary tube after a finger prick and the stopwatch is started. The formation of fibrin staring is noted by breaking the capillary tube at regular intervals. The time is noted at the first appearance of the Fibrin staring.
Requirements
- Sterile lancet
- Capillary tubes (1.5 mm diameter and 10-15 cm length).
- Cotton
- Spirit or 70% alcohol
- Stopwatch
1. Capillary method procedure
- By using a piece of cotton, apply spirit or 70% alcohol to the patient’s fingertip.
- Make a deep 1 mm incision with a sterile lancet and start the stopwatch.
- Wipe off the first blood drop and collect blood in the capillary up to 2 /3rd of the length.
- After every half minute, break off about 1 cm of the capillary to find out whether fibrin string has formed.
- When the fibrin string appear, stop the stopwatch and note down the time.
Advantage
Can be performed when venous blood can not be obtained.
Disadvantage
- Method is insensitive.
- Method is unreliable.
Determination of Clotting time by Lee-White method
Principle
Venous Blood is collected in a clean and dry test tube without anticoagulant. The time required for clotting of the blood is noted.
Method
LEE-WHITE method
Normal Range
5-12 minutes
Requirements
- Sterile lancet or needles
- Cotton
- Spirit or 70% alcohol
- Stopwatch
- Water bath
Procedure
- Collect about 2 ml of blood in the syringe and dispense about 1.0 ml in each of the 2 test tube and start the stopwatch.
- Plug tubes with cotton and keep them in the water bath at 37 degree Celsius.
- After every half minute, by tilting the tube, find out whether the blood has clotted.
- When the blood has clotted in one tube note the time and confirm clotting in the second tube.
Advantage
- More accurate and standard method.
- Test can be run with control
Disadvantage
- It is also a rough method
- There can be contamination of syringe or tubes.
