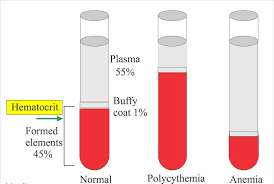
PCV ( packed cell volume ) is the amount of packed red blood cells following centrifugation expressed as percentage of the total blood volume . Packed Cell Volume (PCV) or Hematocrit (HCT) test performe by various following Methods.
- Macro – Hematocrit method
- Micro hematocrit Method
Hematocrit ( HCT ) Test
Hematocrit (HCT) Test By Macro – hematocrit
Clinical significance : –
Fall of hematocrit value are observed in
- Anemias
- Hydremia ( Excessive fluid in the blood as occurs in pregnancy ) .
Increase in hematocrit value are observed in
- Polycythemia
- Dehydration
- Emphysema
- Congenital heart disease .
Method : –
Macro – hematocrit
Normal value : –
| Male | 42 – 52 % |
| Female | 36 – 48 % ( Late pregnancy = 23 – 37 % ) |
Principle : –
when anticoagulant blood is centrifuged in a hematocrit tube at high speed the erythocytes sediment at the bottom . The red cell column is called as packed cell volume ( PCV ) or hematocrit ( cell volume percent ) .
Requirements : –
- specimen EDTA or double oxalate blood ( The specimen need not be a fasting sample ) .
- Wintrobe hematocrit tube
It is 110 mm long tube with a 3 mm internal bore . It is graduated from 0 up to 100 mm ( 10 CM ) . The scale with the descending order is used for pcv determination .
- pasteur pipette or a syringe with needle
- centrifuge machine .
Procedure : –
- Mix the blood sample carefully .
- Label a wintrobe tube .
- Fill the tube by using Pasteur pipette or a syringe up to the 100 mark ( use a needle of wide bore to prevent mechanical breakdown of red blood cells ) . Avoid trapping of air bubbles .
- place the tube in a centrifuge cup ( use another empty wintrobe tube to fill the oposite cup or a tube filled with another specimen ) .
- Centrifuge for 30 minutes at 3000 RPM .
- Note the redding of hematocrit . If the blood is above the 10 mark calculate the cell pack by dividing the height of the column of the packed erythrocytes by the total height of the cell column and plasma .
- Note the following observations
| Color and opacity of plasma | Expected clinical conditions |
| yellow | May be jaundice |
| Milky | Lipemia |
| Cloudy | May be multiple myeloma |
| Reddish | Hemolysis |
Buffy layer : –
Normally it is 0.5 to 1 mm . Each 0.1 ml = 1000 cells per Cumm ( microlitter ) ( approximately ) .
Precaution : –
It is necessary to wash wintrobe tubes immediately after the test by introducing a thick steel wire repeatedly in the tube under running tap water .
Hematocrit (HCT) Test By Micro – hematocrit
In the case of difficulty in drawing sufficient amount of blood micro – hematocrit mathod is used . It is useful particularly in pediatric patients . The method is ideal for skin puncture .
Specimen : –
EDTA or oxalate specimen ( use plain capillary tube ) .
capillary blood ( use heparinized capillaries ) .
Principle : –
Blood is centrifuged in a sealed capillary tube and PCV is determined by a special hematocrit reader .
Estimation of Hemoglobin by Sahli method .
Requirements : –
- Hematocrit centrifuge
It runs at high speed and produce RCF of 12,000 × g and runs at a speed of about 15,000 RPM . It contains a head to hold the capillary tubes .
- Hematocrit reader
This is supplied by the manufacturer .
- Capillary hematocrit tubes
These are 75 mm in length with approximately 1 mm diameter .
- soft wax or modelling clay
This is used to seal the end of the hematocrit tube .
Procedure : –
- Draw the specimen into an appropriate capillary tube . Fill in the tube to about 3/4 length .
- Seal both the ends of the tube with soft wax or modelling clay . It is plugged to a depth of about 1 centimetre .
- write identification number on the tube by using a marking pencil .
- Place the tube with another similar tube in the radial grooves of the centrifuge head exactly opposite to the centrifuge head exactly opposite to each other ( empty capillary tube also can be used ) .
- close the centrifuge cover and centrifuge the tubes at high speed ( about 15,000 RPM ) for 5 minutes .
- Remove the capillary tube . It will show three layers –
- clear plasma at the top
- whitish buffy coat at the middle and
- colymn of red cells at the bottom .
- Hold the tube against the hematocrit scale so that the bottom of the column of red cells is aligned with the horizontal zero line ( exclude the height of clay ) .
- Move the tube across the scale until the line marked 1.0 passes through the top of the plasma column .
- The line that passes through the top or the column of red cells gives the value of PCV ( hematocrit ) .
Source of Error : –
- Hemolyzed specimen will yield false low values .
- Inadequate mixing of blood and incompleteness of packing may lead to erroneous results .
Disadvantages : –
It requires a special centrifuge and disposable capillary tubes .
Additional observation : –
Note any abnormal findings such as
- The color of plasma ( yellow may be for jaundice and reddish for hemolysis ) .
- Increased Buffy coat for increased white blood cells .
