A skeleton system is the internal framework of an organism that provides support and protection for the body’s soft tissues and organs. In vertebrates, the skeleton is made up of bones, while in invertebrates, the skeleton may be made of other materials such as chitin or calcium carbonate. Skeletons also play a role in movement by providing attachment points for muscles. Introduction to The skeleton system
Introduction to The skeleton systems
Skeletons can be classified into two main types: internal and external. Internal skeletons, such as the human skeleton, are found inside the body and are made up of bones, cartilage, and other connective tissue. External skeletons, such as the exoskeleton of an insect or crustacean, are found on the outside of the body and provide protection and support.
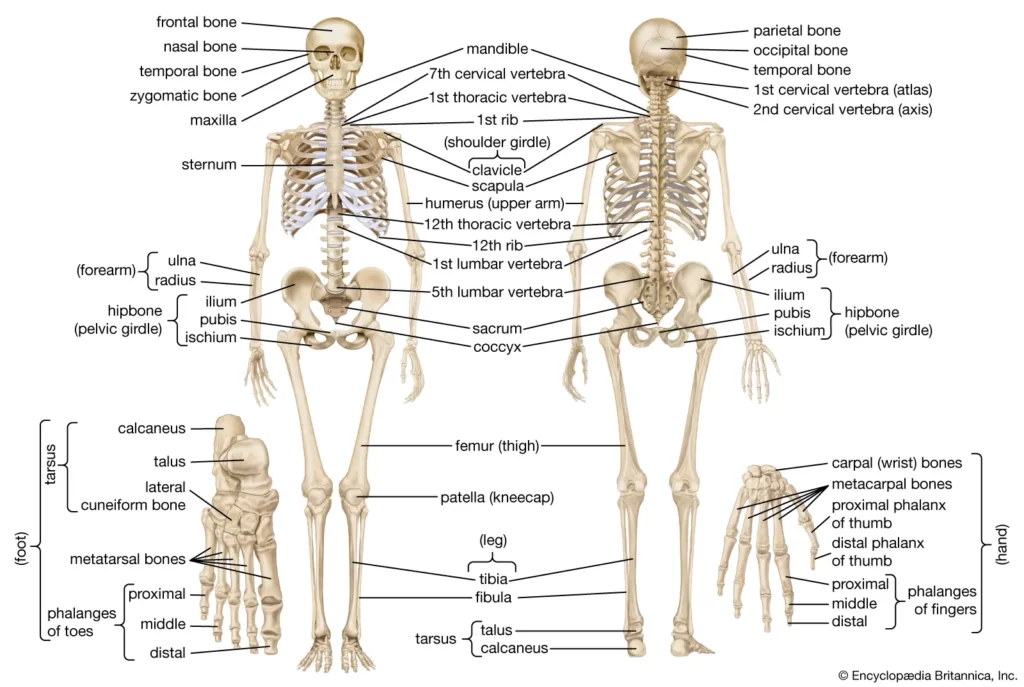
The human skeleton consists of 206 bones, which are divided into two main categories: axial and appendicular. The axial skeleton includes the skull, spine, and rib cage, while the appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the limbs and the shoulder and pelvic girdles.
The skeleton also plays a role in movement by providing attachment points for muscles. Muscles contract and relax to produce movement, and they are attached to bones by tendons. The bones of the skeleton act as levers, which allow the muscles to produce movement.
Overall, the Skeleton system is important for providing support and protection for the body, movement, and also for producing blood cells and storing minerals.
Anatomy of Human skeleton
The human skeleton is made up of 206 bones, which are divided into two main categories: axial and appendicular.
The axial skeleton includes:
- Skull: which protects the brain and includes the facial bones, cranium, and jaw.
- Spine: which runs from the base of the skull to the pelvis and includes the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae, as well as the sacrum and coccyx.
- Rib cage: which surrounds and protect the lungs and heart.
The appendicular skeleton includes:
- Upper limbs: which consist of the shoulder girdle, made up of the scapula and clavicle, and the arm, forearm, and hand bones
- Lower limbs: which consist of the pelvic girdle, which is made up of the hip bones, and the thigh, leg, and foot bones.
Bones are connected to each other by joints, which allow for movement. Some joints are immovable, such as the joints between the skull bones, while others are highly mobile, such as the joints in the shoulder and hip. The bones also have various features like foramina, process, head, neck, fosse etc.
The skeleton also plays a role in the production of blood cells and the storage of minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus. The bone marrow inside the bones produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, and the bones also store minerals that can be released into the bloodstream as needed.
Structure of Skeleton System
The structure of the skeleton system can be divided into two main categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
The axial skeleton is the central core of the body and includes the skull, vertebral column (spine), and rib cage. The skull is composed of the cranial bones that surround and protect the brain and the facial bones that make up the face, jaw, and teeth. The vertebral column is made up of individual vertebrae stacked on top of each other. It runs from the base of the skull to the pelvis and is divided into regions such as the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar. The rib cage surrounds and protect the lungs and heart.
The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the limbs and the girdles that connect the limbs to the axial skeleton. The girdles are the pelvic girdle, which is made up of the hip bones, and the shoulder girdle, which is made up of the scapula and clavicle. The upper limb includes the arm, forearm, and hand bones, and the lower limb includes the thigh, leg, and foot bones.
Each bone has its own unique shape, size and structure. Some bones are long and slender, such as the bones of the arms and legs, while others are short and wide, such as the bones of the skull and pelvis. Some bones are flat, such as the sternum, while others are irregular, such as the vertebrae.
Overall, The structure of the skeleton system is made up of bones that are connected to each other by joints, allowing for movement, and also have various features that have different functions. The bones also provide protection for vital organs and support for the body.
The human skeleton is divided into two main regions: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
The axial skeleton includes the skull, spine, and rib cage. The skull is made up of the cranial bones that surround and protect the brain and the facial bones that make up the face, jaw, and teeth. The spine, also known as the vertebral column, runs from the base of the skull to the pelvis and is divided into regions such as the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar. The rib cage surrounds and protect the lungs and heart.
The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the limbs and the girdles that connect the limbs to the axial skeleton. The girdles are the pelvic girdle, which is made up of the hip bones, and the shoulder girdle, which is made up of the scapula and clavicle. The upper limb includes the arm, forearm, and hand bones, and the lower limb includes the thigh, leg, and foot bones.
I hope this helps you to understand the main bones and regions of the human skeleton, if you need a diagram, you can find many on internet or in anatomy books.
Name of Bone
There are 206 bones in the human body, and they can be divided into several categories: skull bones, facial bones, vertebrae, rib bones, breastbone, shoulder bones, arm bones, hand bones, pelvic bones, thigh bones, leg bones, and foot bones. Some examples of bones in the human body include:
- Cranial bones: frontal bone, parietal bones, temporal bones, occipital bone, sphenoid bone, ethmoid bone
- Facial bones: mandible, maxilla, nasal bones, lacrimal bones, zygomatic bones, palatine bones, vomer, inferior nasal conchae
- Vertebrae: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx
- Rib bones: true ribs, false ribs, floating ribs
- Breastbone: sternum
- Shoulder bones: scapula, clavicle
- Arm bones: humerus, radius, ulna
- Hand bones: carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
- Pelvic bones: illium, ischium, pubis
- Thigh bones: femur
- Leg bones: tibia, fibula
- Foot bones: tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges
These are some examples of bones in the human body, but there are many more bones that make up the skeleton system.
Functions of Skeleton System
The skeleton system has several important functions in the body, including:
- Support: The skeleton provides structural support for the body, allowing us to stand upright and maintain our shape.
- Protection: The skull, rib cage, and pelvic bones protect vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs from injury.
- Movement: The bones of the skeleton act as levers and provide attachment points for muscles, allowing for movement of the body.
- Blood cell production: Bone marrow, the spongy tissue found inside some bones, produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Mineral storage: Bones store minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which can be released into the bloodstream as needed to maintain healthy levels in the body.
- Triglycerides storage : Adipose cells found in the bone marrow can store and release triglycerides.
- Hormone regulation: Some bones such as the skull, spine, and pelvis, contain specialized cells that can produce and secrete hormones that regulate various physiological processes in the body.
- Respiration: Ribs and diaphragm play a role in the breathing process.
Overall, the skeleton system is essential for maintaining the body’s structure, protecting vital organs, facilitating movement, producing blood cells, and storing minerals, as well as playing a role in hormone regulation and respiration.
Fact of the Skeleton System
Here are some interesting facts about the skeleton system:
- The human skeleton is made up of 206 bones, which are held together by ligaments and tendons.
- The skull is made up of 22 bones, the spine is made up of 33 bones, and the rib cage is made up of 24 bones.
- The longest bone in the body is the femur, located in the thigh, and the smallest bone is the stapes, located in the ear.
- The skeleton is not a static structure and it is continuously undergoing remodeling process through life.
- The bones in the body are not solid, they contain a network of blood vessels and hollow spaces that are filled with bone marrow.
- The bones in the body are not always white, they can also be black, yellow, or even red.
- The human skeleton is able to withstand a force of up to 20 times the body weight.
- The patella, or kneecap, is the only bone in the body that is not attached to any other bone.
- The sternum or breastbone is the only moveable bone in the rib cage.
- A person’s bones become stronger during the teenage years and reach their maximum strength and density in their early 20s.
Overall, The skeleton system is an intricate and complex structure that plays a vital role in the body’s functions and it has many interesting characteristics.
