What is Anatomy And Physiology
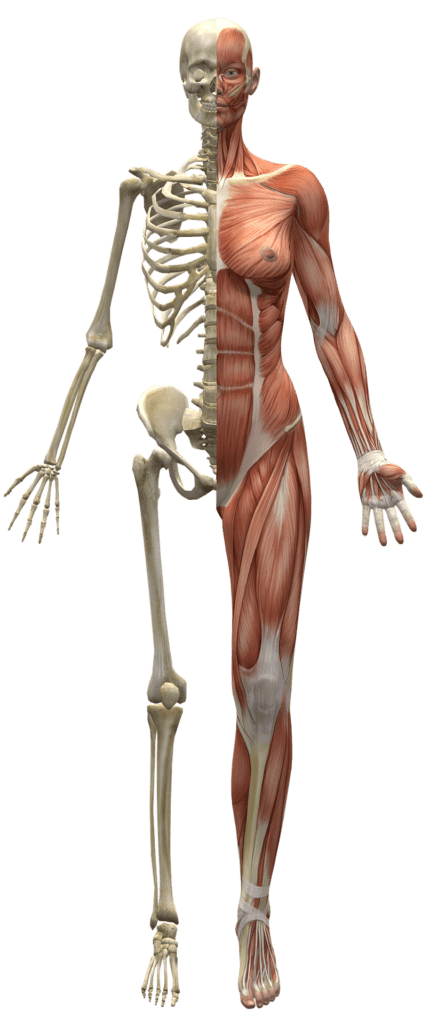
Anatomy:-
Anatomy is the study of the structure and organization of living organisms. It can be divided into two main branches: gross anatomy, which focuses on the study of the body’s major systems and organs, and microscopic anatomy, which focuses on the study of cells and tissues. Anatomy is a key component of the medical field, as a thorough understanding of the body’s structure is essential for diagnosis and treatment of injuries and illnesses.
Branches of Anatomy
There are several branches of anatomy, each focusing on a different aspect of the body’s structure and function. Some of the main branches include:
- Gross Anatomy: This branch of anatomy deals with the study of the body’s major systems and organs, such as the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and cardiovascular systems.
- Microscopic Anatomy: This branch of anatomy deals with the study of cells and tissues, including their structure, function, and interactions.
- Developmental Anatomy: This branch of anatomy deals with the study of how the body develops from the embryonic stage to adulthood.
- Comparative Anatomy: This branch of anatomy deals with the study of the similarities and differences in the structure and function of different species.
- Pathological Anatomy: This branch of anatomy deals with the study of how diseases and disorders affect the body’s structure and function.
- Radiological Anatomy: This branch of anatomy deals with the study of the body’s internal structures as they appear on diagnostic imaging such as x-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound and other imaging modalities.
- Neuroanatomy: This branch of anatomy deals with the study of the structure and function of the nervous system.
- Embryology: This branch of anatomy deals with the study of the development of an organism from the fertilized egg to the fetus stage.
These branches of anatomy are interrelated and mutually dependent on each other to have a complete understanding of the human body.
Human Body Systems
Name of Human Body systems:-
There are several systems in the human body, including:
- The skeletal system, which provides support and protection for the body
- The muscular system, which allows for movement and generates heat
- The cardiovascular system, which circulates blood and oxygen throughout the body
- The respiratory system, which brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide
- The nervous system, which coordinates and controls various bodily functions
- The digestive system, which breaks down food and absorbs nutrients
- The endocrine system, which produces hormones that regulate various bodily processes
- The urinary system, which removes waste products from the body
- The immune system, which defends the body against disease and infection.
- The reproductive system, which allows for the production of offspring
- The lymphatic system, which helps to defend the body against infection and disease by removing excess fluids and waste products, and by producing immune cells
- The integumentary system, which includes the skin, hair, and nails and serves as a barrier against external elements, helps to regulate body temperature, and produces vitamin D when exposed to sunlight.
- The Skeletomuscular system which includes muscles and bones together, it allows movement and support to the body.
- The sensory system which includes the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin and responsible for receiving and interpreting information from the environment.
- The vestibular system which is responsible for balance and spatial orientation.
- The cerebrovascular system which is responsible for blood circulation in the brain.
- The endocannabinoid system which is responsible for maintaining homeostasis within the body.
Human Physiology
Human physiology is the study of the functions and mechanisms of the human body. It encompasses a wide range of systems and processes, including the nervous, muscular, skeletal, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems. It also includes the study of hormones, metabolism, and genetics. Understanding human physiology is essential for understanding how the body works and for diagnosing and treating illnesses and injuries.
Branches of Physiology
There are several branches of physiology, including:
- Cell physiology: Studies the functions and mechanisms of individual cells and their organelles.
- Systems physiology: Studies the functions and interactions of the body’s organ systems, such as the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
- Comparative physiology: Studies the physiological differences and similarities among different species.
- Environmental physiology: Studies the effects of the environment on the body, such as the effects of pollution and extreme temperatures.
- Pathological physiology: Studies the changes in the body’s systems and processes that occur as a result of disease or injury.Exercise physiology: Studies the effects of exercise on the body.
- Developmental psychiatry: Studies the physiological changes that occur during fetal development, infancy, childhood, and adolescence.
- Integrative physiology: Studies the integration of various physiological systems and processes to maintain homeostasis and health.
- Molecular physiology: Studies the molecular basis of physiology and its relationship with the physiology.
- Clinical psychiatry: Studies the diagnosis and treatment of physiological disorders in patients.
These are some of the broad categories, There are many sub-branches and specialties within each of these areas of study.
