what is leukopoiesis ?
Leukopoiesis :- Leukopoiesis is production of white blood cells. It has three independent series which lead to the formation of –
- Granulocytes
- Lymphocytes
- monocytes
Granulocytes :-
The granulocytes are formed in the marrow and the process of Maturation is divided into six stages. In this series the cytoplasm develops specific granules as the cell matures and the progressive maturation of the nucleus is indicated by segmentation . The stem cell or R.E. cell gives to other type of cell .
Development of neutrophil
From the primitive precursor, pluripotent stem cell develops the committed stem cell and from this develops the progenitor cell , which is called colony forming unit , granulocytes monocytes ( CFU , GM ) . It is the common ancestor of both the neutrophil as well as the monocytes. CFU , GM produces either the myeloblast ( precursor of neutrophil ) or the monoblast ( precursor of monocytes,) .
Myeloblast :-
Myeloblast is a big sized cell ( 15 to 20 micrometre ) with a very big nucleus which almost completely fills up the cell leaving a peripheral rim of cytoplasm . Nucleus contains 1 to 5 nucleoli and the cytoplasm is nongranular .
Promyeloblast :-
Promyeloblast which forms later resembles a myeloblast except that the cytoplasm appears pink colored with nonspecific red granules . It contains one or two less defined nucleoli and coarse chromatin .
Myelocyte :-
Myelocyte formation takes place , which is smaller in size and contains round or oval nucleus with larger pink cytoplasm . The nucleoil disappears and cytoplasm of this cell contains numerous specific purple , red or blue colored granules .
Neutrophil :-
The myelocyte then undergoes further maturation and become a neutrophils . The nucleus of a neutrophil contains several lobes . The number of lobes increases as the cell grows older . In healthy state , maximum number of lobes in a neutrophil can be about seven . Neutrophil contain fine cytoplasmic granules . The diameter of neutrophils range between 10 – 12 micrometre and Amobid shape . It’s life 1 – 2 days life span in circulation .
| Normal value | 40 – 75 % |
| Absult value | 3000 – 6000 / Cumm ( microlitter ) |
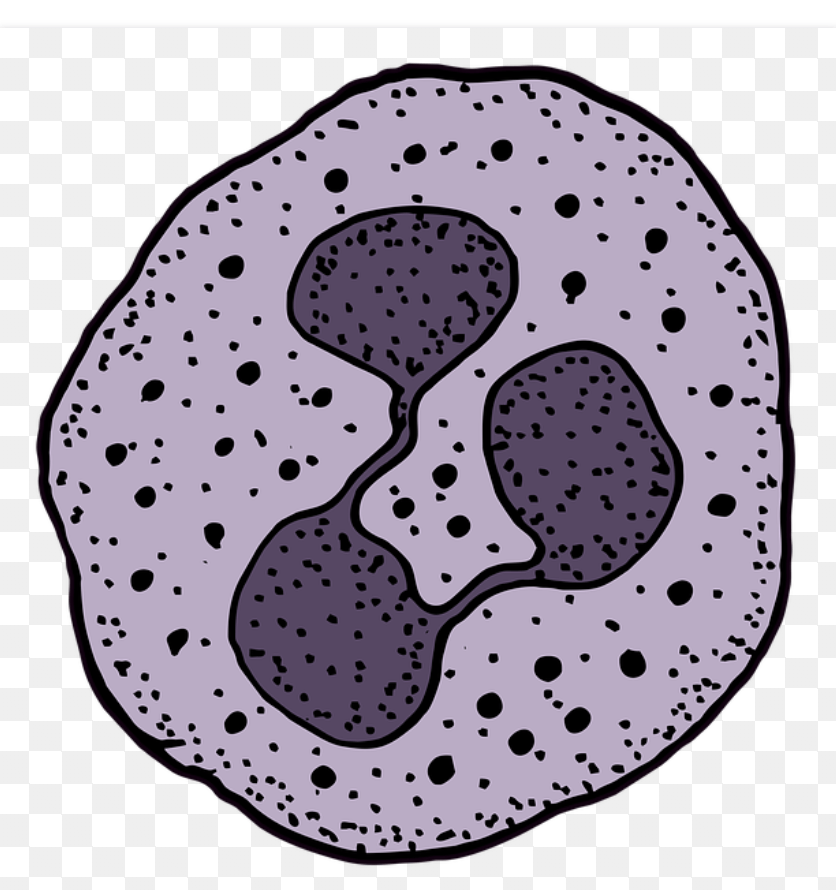
Development of Eosinophil
From the progenitor cell , develops the eosinophilc myeloblast , which in turn develops into myelocyte and then into mature eosinophil . The eosinophil nucleus is bi- lobes . Eosinophils contain fine cytoplasmic granules . The diameter of Eosinophils range between 10 – 14 micrometre . It’s 1 – 2 days life span in circulation .
| Normal value | 1- 6 % |
| Absult value | 40 – 440 / Cumm |
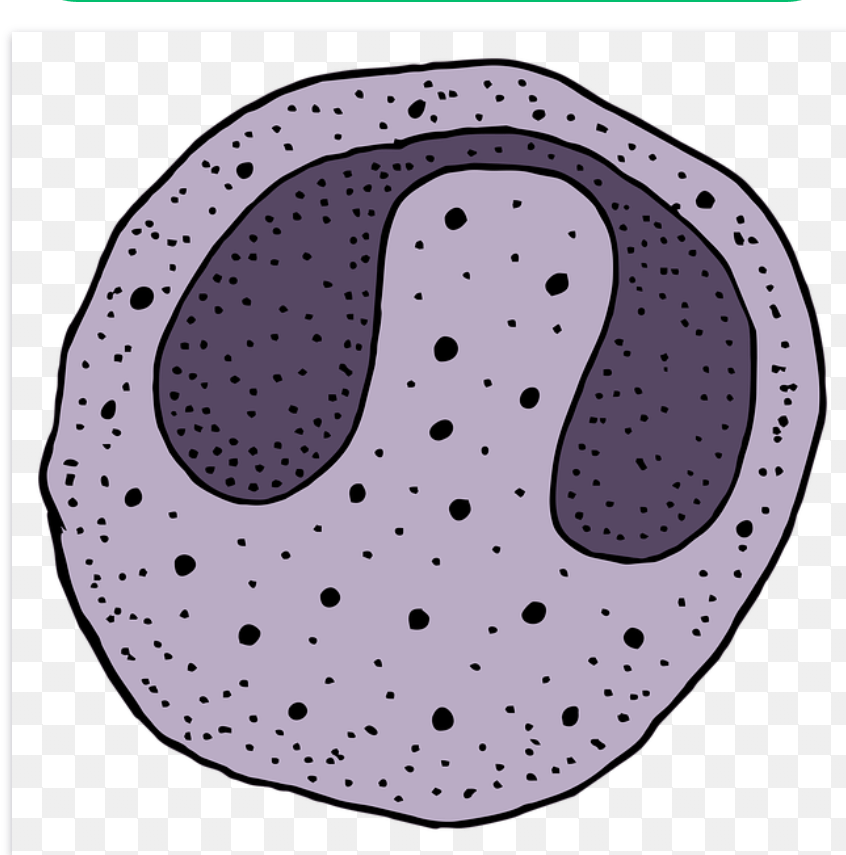
Development of monocytes
Monoblast is the earlier recognizable cell which develops into the promonocyte and then into monocyte . The nuclei of monocytes are not segmented and are indented ( kidney like ) in shape . The cytoplasm is finely granulated . The cell size is the largest of all the white blood cells seen in peripheral circulation . The monocyte are the biggest of the Leukocytes with nucleus showing indentation . The diameter of monocytes ( non – granular ) between 12 – 20 micrometre . It’s 1day life span in circulation .
| Normal value | 2 – 8 % |
| Absult value | 200 – 600 / Cumm |
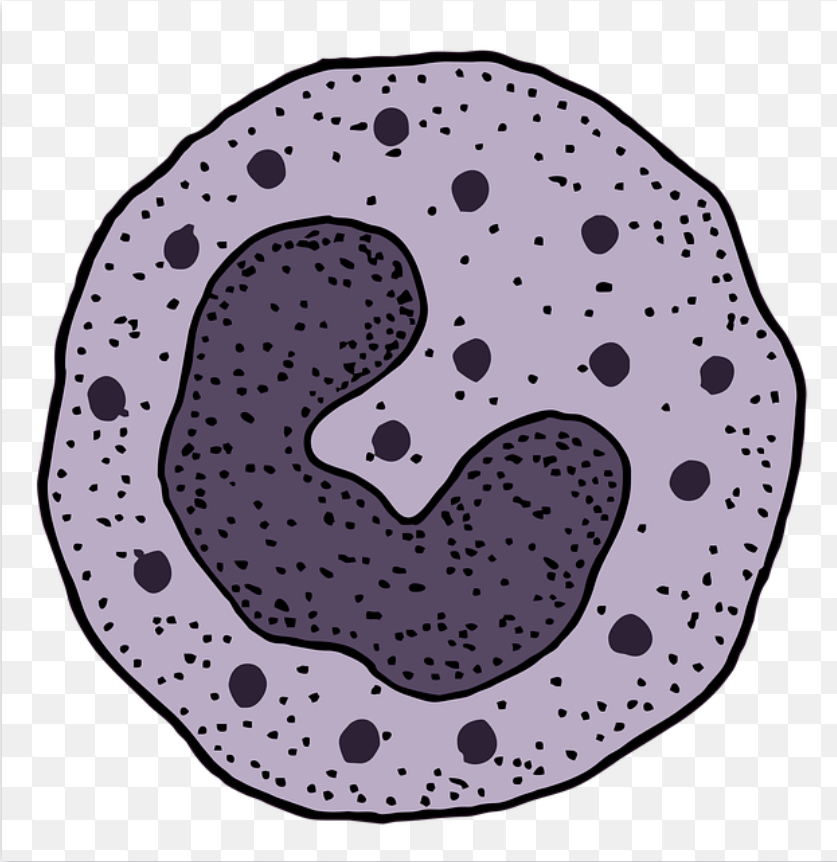
Development of Basophil
The general line of development is similar to the other members of granulocytes from progenitor cell formation of basophilic myeloblast from and from which formation of basophil takes place . Thr basophil nuculeus S shaled . Basophil contain very coarse cytoplasmic granules . The diameter of basophil range between 8 – 10 micrometre . It’s 1 – 2 days life span in circulation .
| Normal value | 0 – 2 % |
| Absult value | 0 – 100 % |
Development of Lymphocytes
Morphologically the lymphocytes are divided as small lymphocytes and large lymphocytes. Functionally , however , the lymphocytes are divided into two classes , Viz , T lymphocytes ( from thymus ) and B- lymphocytes ( from bursa of fabricius , which in human is probably the reb bone marrow) . About 70% of Lymphocytes in the peripheral blood are T- lymphocytes and rest of the lymphocytes are B lymphocytes . The development of Lymphocytes takes place as follows :-
- The precurosors of the lymphocytes are present in the red bone marrow. During the fetal life , from red bone marrow some lymphocytes precursors and become T lymphocytes , which are immunologically competent .
- These T lymphocytes go to the peripheral lymphoid tissue ( lymphoid tissue in tonsils , lymph nodes , etc . ) From there they make back and forth journey to blood .
- Some T lymphocytes become memory cells within the lymph nodes . On receiving a fresh antigenic challenge , T lymphocytes are supplied by the memory cell .
- Another precursor goes to the central lymphoid tissue ,( in human , it is most probably red bone marrow ) . From here they move to the peripheral lymph nodes and known as B lymphocytes . They also have memory cells which multiply and produce new cells on receiving an antigenic challenge . The nucleus is not lobed . In lage Lymphocyte the amount of cytoplasm is comparatively larger . The diameter of Lymphocytes between 7 – 10 micrometre .
| Normal value | 20 – 40 % |
What is Leukocytes ?
The Leukocytes or white blood cells ( WBC ) are nucleated corpuscles . In healthy adults , the number of leukocytes is between 5000 and 10,000 / Cumm (microlitter ) of blood . The various types of white blood cells found in a circulating blood are given below :

This classification is based upon certain Morphological characteristics of the lymphocytes. When a blood film is stained using a staining solution Leishman stain containing methylene blue ( a basic dye ) and eosin ( an acidic dye ) , the nucleus is stained blue by the basic dye . The granules present in some type of leukocytes may be eosinophilc , basophilic or neutrophilic . Accordingly and neutrophils , respectively . The Leukocytes containing granules are called granulocytes and those who do not contain granules are nongranulocytes .
Functions and properties of Leukocytes
- Leukocytes are needed by the body for its defense against invading organisms like bacteria , viruses , parasites and cancer cells .
- It is mainly the Neutrophils and the monocytes that attack and destory viruses and bacteria in the circulating blood .
- Although blood monocyte have little ability to fight infectious agents , once they enter the tissue they begin to swell and develop large numbers of lysosomes in the cytoplasm .
- These cells are called macrophages which are capable of combating disease agents .
- Plasma cells which are derived from lymphocytes , produce immunoglobulins which neutralized the toxins produed by invading organisms .
- Neutrophils are called upon to act in acute infections . When there is an acute infection , neutrophils promptly come to the spot , Cordon the area , phagocytic the organism and the digest them .
- The lysosomes present in neutrophils carry a large number of proteolytic , amylolytic , lipolytic enzyme and also other enzymes such as nucelotidases and catalase .
- The invading organisms destroy some local tissues which produce some chemicals , notably histamine , serotonin and bradykinin .
- These substances cause vasodilation of the local area .
- The circulating neutrophils adhere to the margins of the blood vessels and come out to act by throwing their pseudopodia into the pores in between the endothelial cells of the capillaries .
- The circulating monocytes leave the intravascular compartment and from tissue macrophage . These macrophages ingest mainly those bacteria which commonly produce chronic infections .
- They also phagocytize tissue debris , organic and inorganic chemicals and even cancer cells .
- Giant cells are formed when several macrophages coalesce together .
- Lympocytes are responsible for the phenomenon called immunity . B lympcytes are ultimately converted into plasma cell which produce immunoglobulins .
- These are present in the gammaglobulin fraction of plasma proteins the immunoglobulins combine with and neutralize bacteria and various toxic materials produced by invading organisms .
- Cellular immunity is produced by T lymphocytes . These cells combine directly with the bacteria , viruses , cancer cells and destroy them .
- Eosinophils cells rise in number in allergic disorder and also in parasitic infections .
- The eosinophils can ingest antigen – antibody complexes , neutralize histamine and dissolve clots .
- A protein called major basic protein present in the eosinophils destroys the larval parasites .
- The basophilis of the blood contain histamine , serotonin and heparin .
- In the tissue identical mast cells are present .
- During information , histamine , serotonin and bradykinin are liberated by the damaged basophilis as well as by the mast cells . Histamine and serotonin are powerful vasodilators .
