What is Microbiology
Introduction:-
The science Of Microbiology Is the Study of Microorganism and their activities. It is Concerned with their (1) Form (2) Structure (3) Physiology (4) Metabolism (5) Identification and (6) Reproduction. The microorganisms are called as protesta. This class includes all. Unicellular organisms. Which are? Characterised to buy. There lack of definite. Cellular arrangement as well as lack of differentiation of the cells for specific metabolic function. The microorganism. Include in the Kingdom Protista are:-
- Bacteria
- Algae
- Fungi
- Protozoa.
The micro organisms classified as protesta may be further divided into (A) Prokaryotes and (B) Eukaryotes.
A. Prokaryotes Group:-
It contains microorganism. With a very simple cell structure. The cell is not bound by membrane And it does not contain cell defined cellular organelles. The genetic material lies as a single piece of double standard DNA in the cytoplasm. It is not organised into chromosomes inside a nuclear membrane. The cell does not contain mitochondria but contains simple enzyme system. Prokaryotes multiply by a simple dividing process. know as binary fission.
Examples:-
Bacteria including rickettsiae, chlamydiae, Mycoplasma and blue green algae.
The Eukaryotic Group:-
It contains microorganisms with a complex cell structure similar to that of higher organisms. The genetic material of a eukaryotic cell is differentiated into chromosomes which are contained in a nuclear membrane to form a definite nucleus. The cell contains complex enzyme systems, mitochondria and other organelles. The cell is able to make its own energy. Eukaryotes multiply by mitosis.
Examples:-
Protozoa, Fungi, Algae (except blue green algae).
Branches of Microbiology
Microbiology is a broad field that encompasses several subdisciplines, including:-
- Medical microbiology: the take a look at of microorganisms that motive ailment in humans and animals.
- Commercial microbiology: the utility of microbiological concepts and strategies to the manufacturing of products along with meals, antibiotics, and enzymes.
- Environmental microbiology: the study of microorganism in herbal and guy-made environments, together with soil, water, and air.
- Meals microbiology: the look at of microorganisms which might be worried in food production, upkeep, and spoilage.
- Agricultural microbiology: the take a look at of microorganisms that are utilized in agriculture, together with those who assist to restore nitrogen in soil or shield vegetation from sickness.
- Marine microbiology: the look at of microorganisms that stay inside the ocean, including people who play a position within the marine meals internet and biogeochemical cycles.
- Virology: the examine of viruses and the illnesses they reason.
- Mycology: the study of fungi and their roles inside the surroundings, medicinal drug, and industry.
- Immunology: the examine of the immune gadget and how it defends in opposition to infectious retailers.
- Microbial Genetics: the observe of the genetic and molecular biology of microorganisms.
Definition of Medical Microbiology
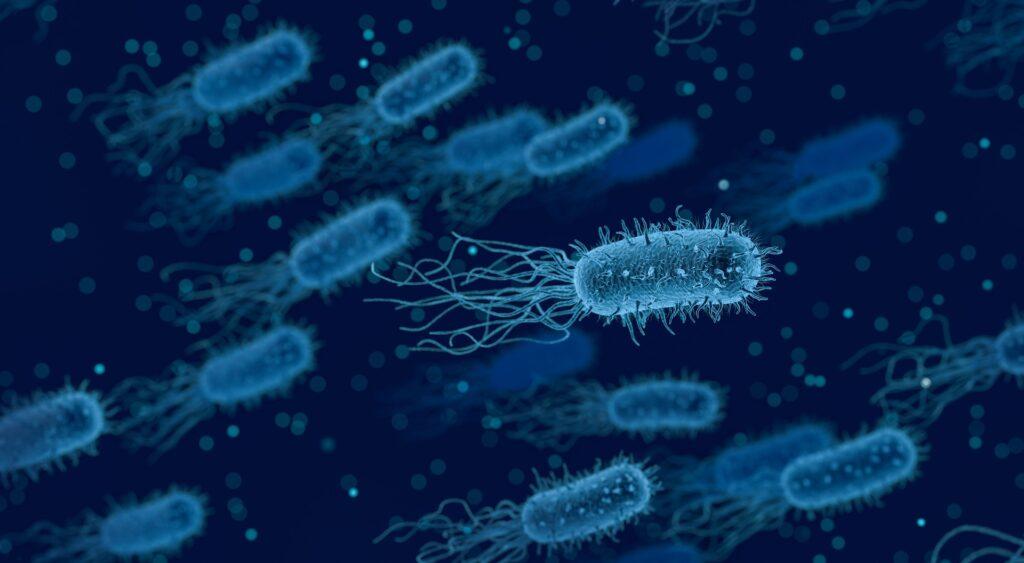
Clinical microbiology is the examine of the function of microorganisms in human fitness and ailment. This includes the examine of micro organism, viruses, fungi, and parasites, and the way they interact with the human frame. Clinical microbiologists use this knowledge to diagnose and treat infections, in addition to to develop new treatments and vaccines. Additionally they play a crucial function in stopping the unfold of infectious diseases.
Definition of Bacteriology
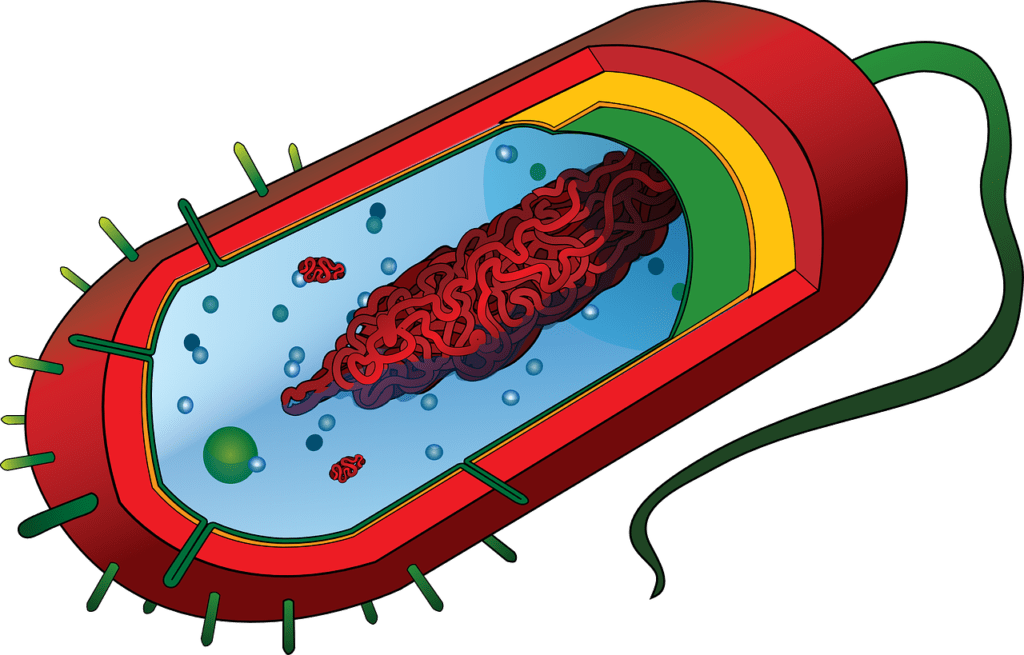
Bacteriology is the precise have a look at of micro organism. An expertise of any organization of organisms requires their. Classifications. Most bacteria aren’t pathogenic. The right category gadget gives a board understanding of courting among unique organisms. In a pathological laboratories successful classification of Pathogenic organisms may additionally offer the direct course to their elimination. The interrelated regions of bacterial Taxonomy.
Definition of Virology
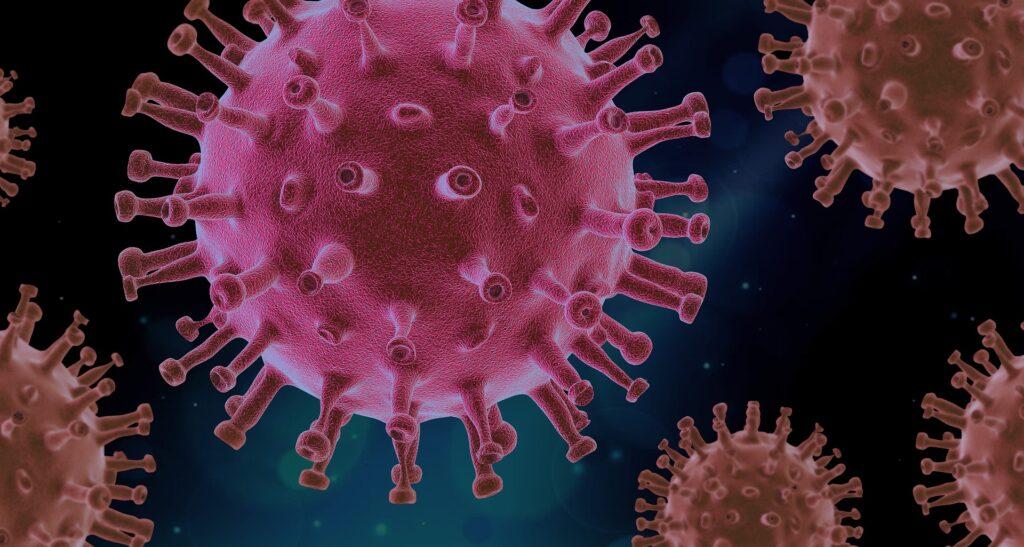
Virology is the study of viruses, including their structure, classification, replication, and pathogenesis (the way they cause disease). It also includes the study of the host immune response to viral infection and the development of antiviral drugs and vaccines.
Definition of Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and distribution, and their use as a source for medicine, food, and other products. It also deals with the diseases that fungi can cause in plants and animals.
Definition of Parasitology

Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. It encompasses a wide range of organisms, including protozoa, helminths, and arthropods, and examines their biology, ecology, and pathogenesis. The field also includes the study of the detection, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of parasitic diseases in humans and animals.
